Observability
Observability enables tracking the inner workings of a system without having to change the system. This makes it much easier to debug and evaluate overall performance.
txtai has an integration with MLflow and it's tracing module to provide insights into each of the components in txtai.
Examples
The following shows a number of examples on how to introduce observability into a txtai process.
Initialization
Run the following sections first to initialize tracing.
# Install MLflow plugin for txtai
pip install mlflow-txtai
# Start a local MLflow service
mlflow server --host 127.0.0.1 --port 8000
import mlflow
mlflow.set_tracking_uri(uri="http://localhost:8000")
mlflow.set_experiment("txtai")
# Enable txtai automatic tracing
mlflow.txtai.autolog()
Textractor
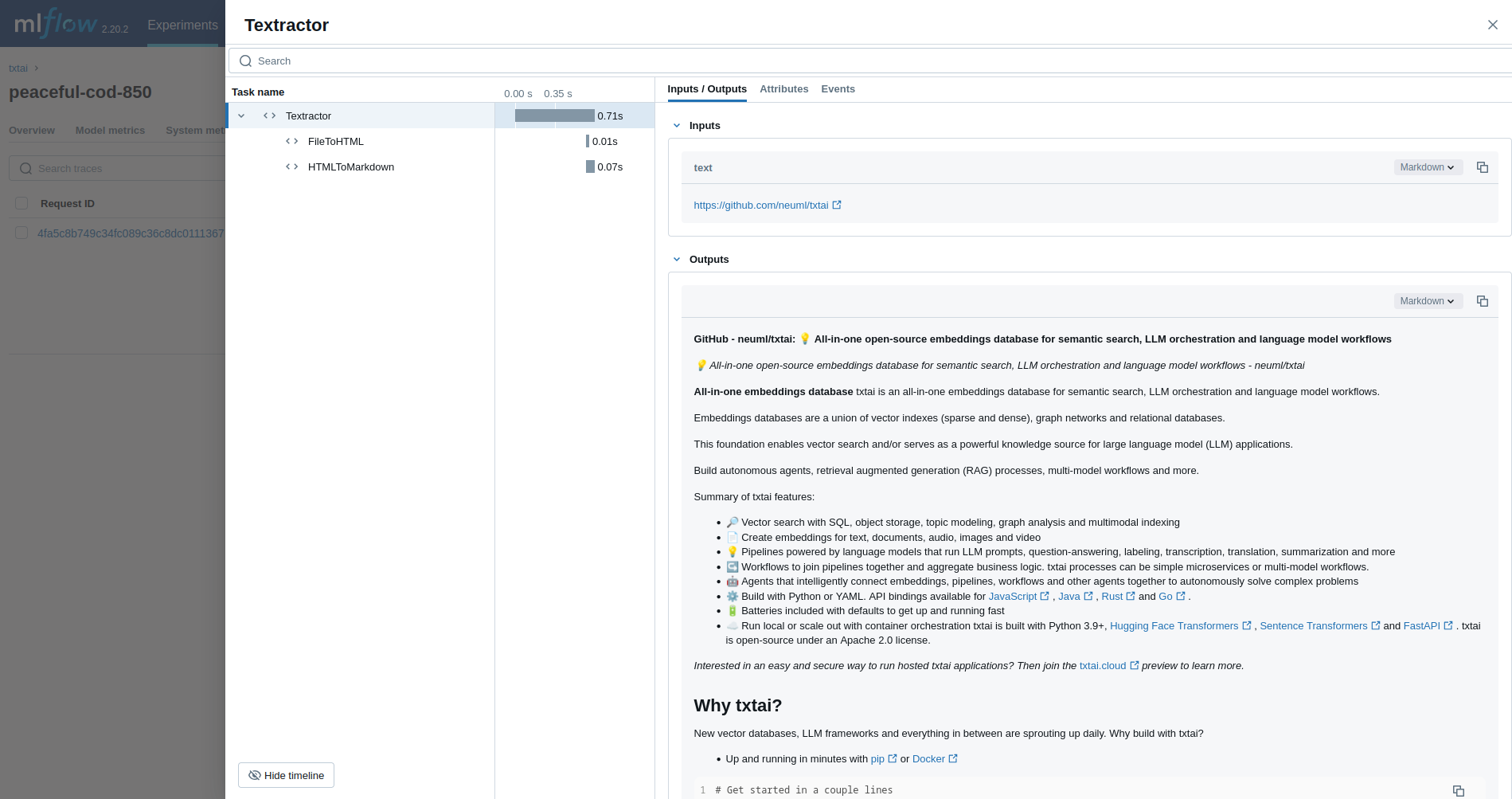
The first example traces a Textractor pipeline.
from txtai.pipeline import Textractor
with mlflow.start_run():
textractor = Textractor()
textractor("https://github.com/neuml/txtai")
Embeddings
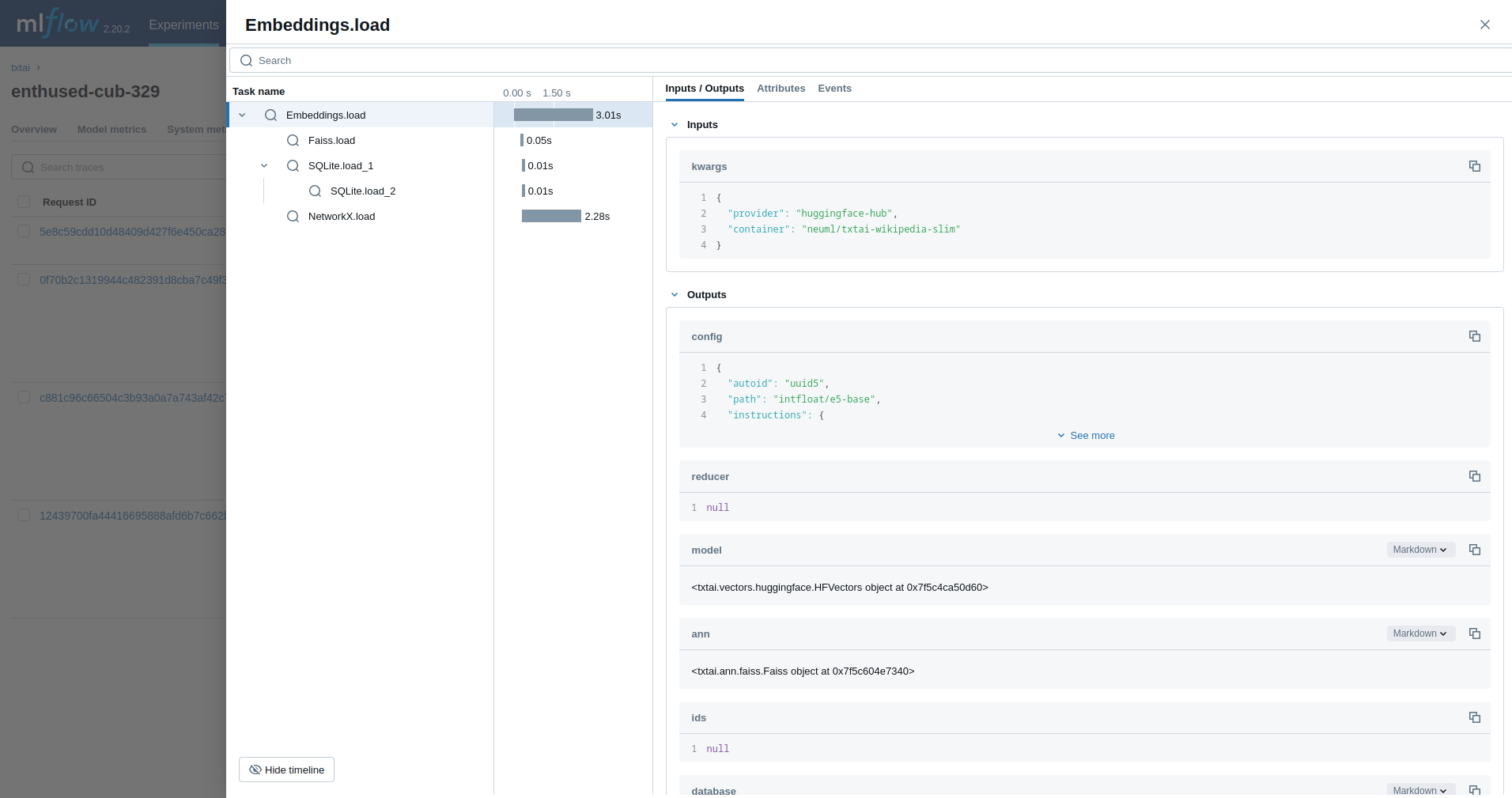
Next, we'll trace an Embeddings query.
from txtai import Embeddings
with mlflow.start_run():
wiki = Embeddings()
wiki.load(provider="huggingface-hub", container="neuml/txtai-wikipedia-slim")
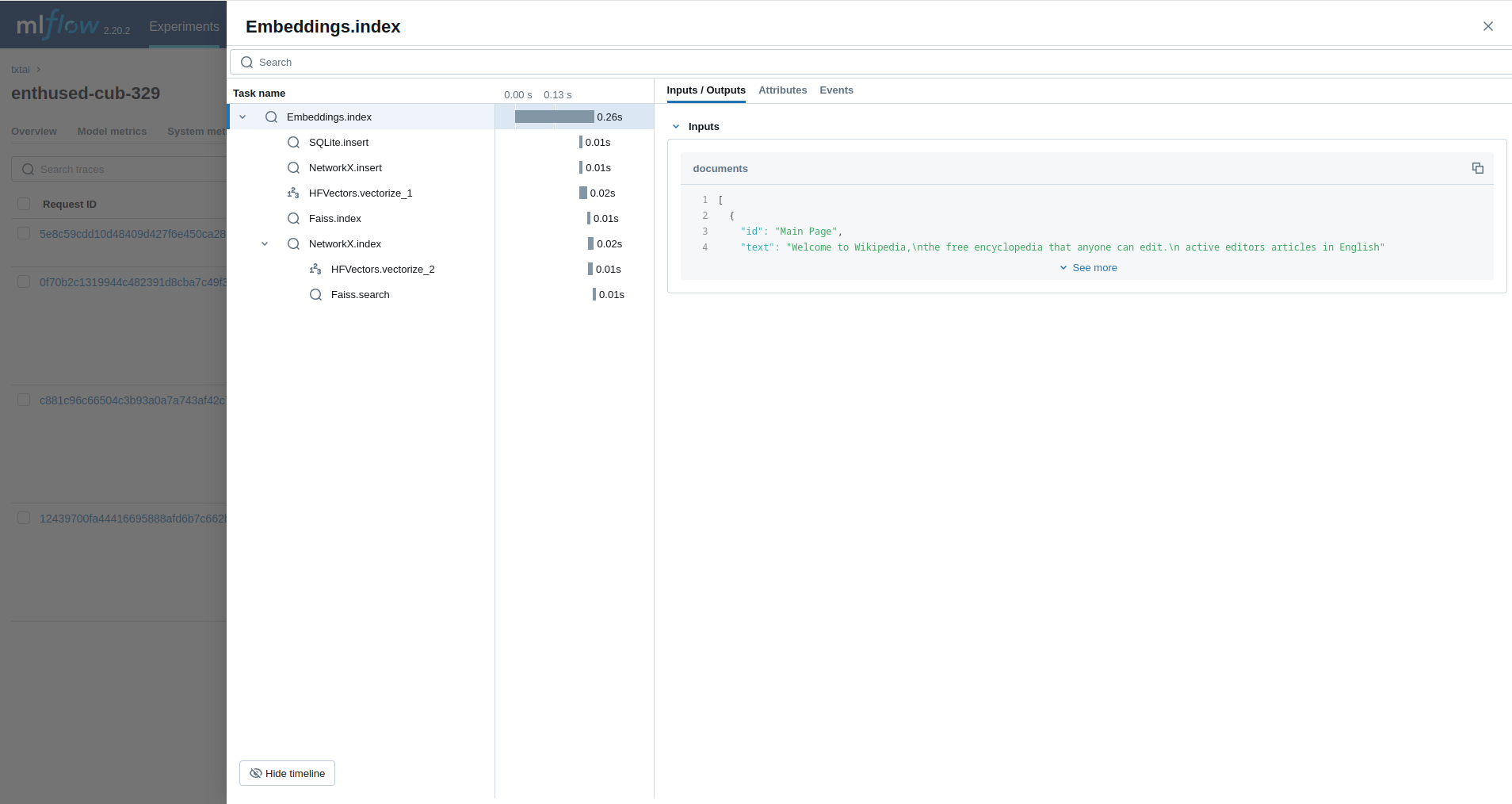
embeddings = Embeddings(content=True, graph=True)
embeddings.index(wiki.search("SELECT id, text FROM txtai LIMIT 25"))
embeddings.search("MATCH (A)-[]->(B) RETURN A")
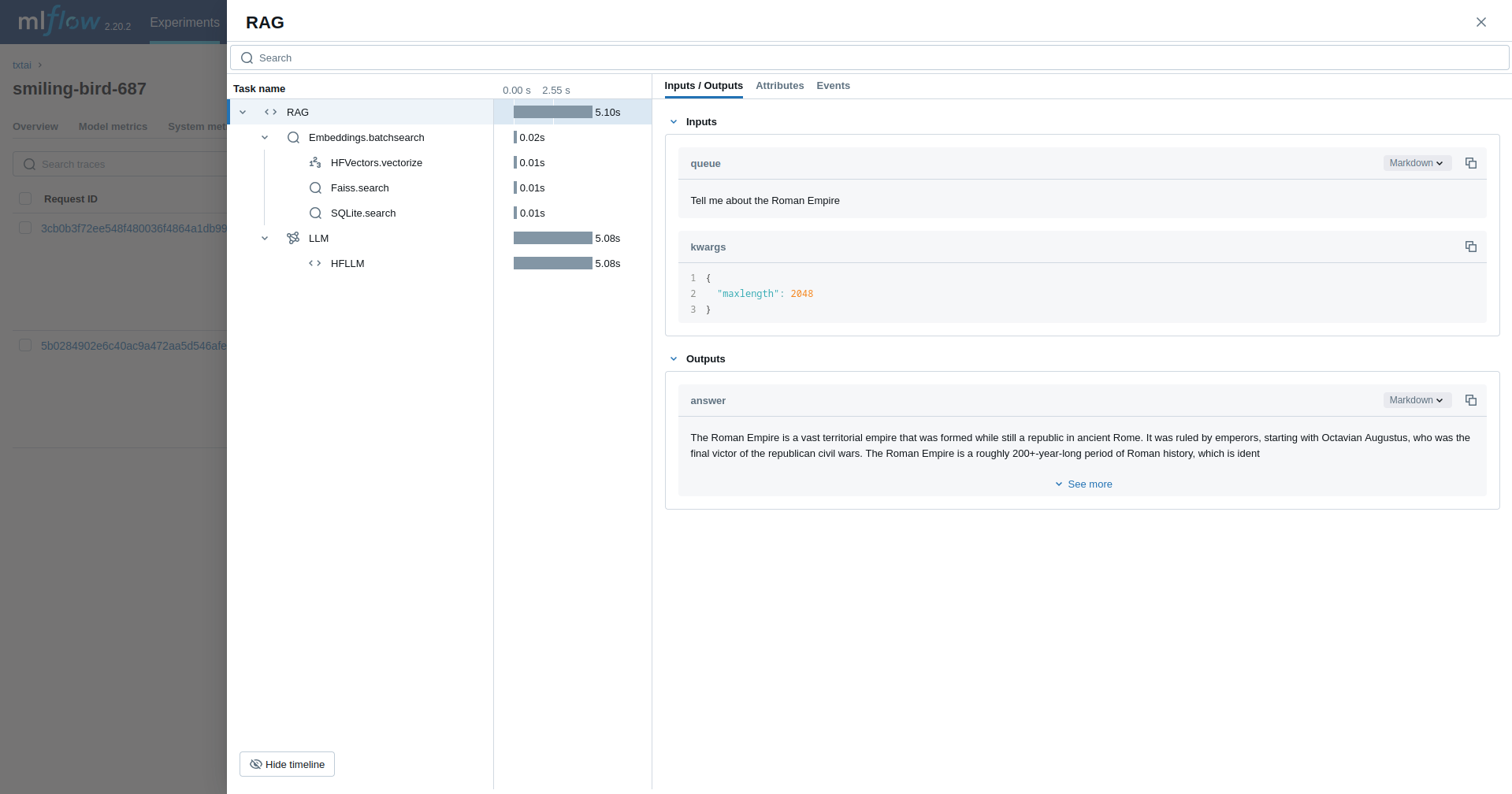
Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG)
The next example traces a RAG pipeline.
from txtai import Embeddings, RAG
with mlflow.start_run():
wiki = Embeddings()
wiki.load(provider="huggingface-hub", container="neuml/txtai-wikipedia-slim")
# Define prompt template
template = """
Answer the following question using only the context below. Only include information
specifically discussed.
question: {question}
context: {context} """
# Create RAG pipeline
rag = RAG(
wiki,
"openai/gpt-oss-20b",
system="You are a friendly assistant. You answer questions from users.",
template=template,
context=10
)
rag("Tell me about the Roman Empire", maxlength=2048)
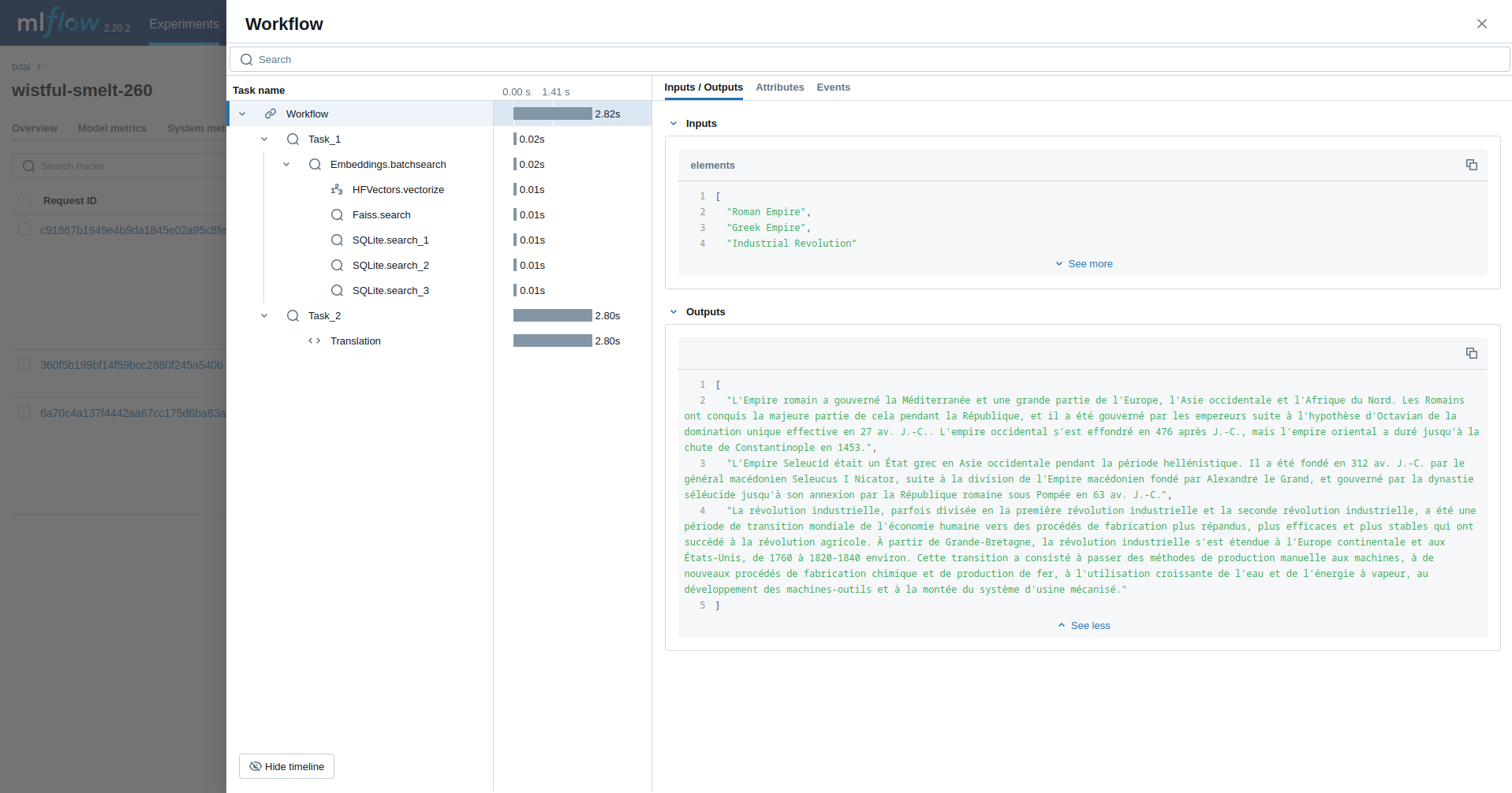
Workflow
This example runs a workflow. This workflow runs an embeddings query and then translates each result to French.
from txtai import Embeddings, Workflow
from txtai.pipeline import Translation
from txtai.workflow import Task
with mlflow.start_run():
wiki = Embeddings()
wiki.load(provider="huggingface-hub", container="neuml/txtai-wikipedia-slim")
# Translation instance
translate = Translation()
workflow = Workflow([
Task(lambda x: [y[0]["text"] for y in wiki.batchsearch(x, 1)]),
Task(lambda x: translate(x, "fr"))
])
print(list(workflow(["Roman Empire", "Greek Empire", "Industrial Revolution"])))
Agent
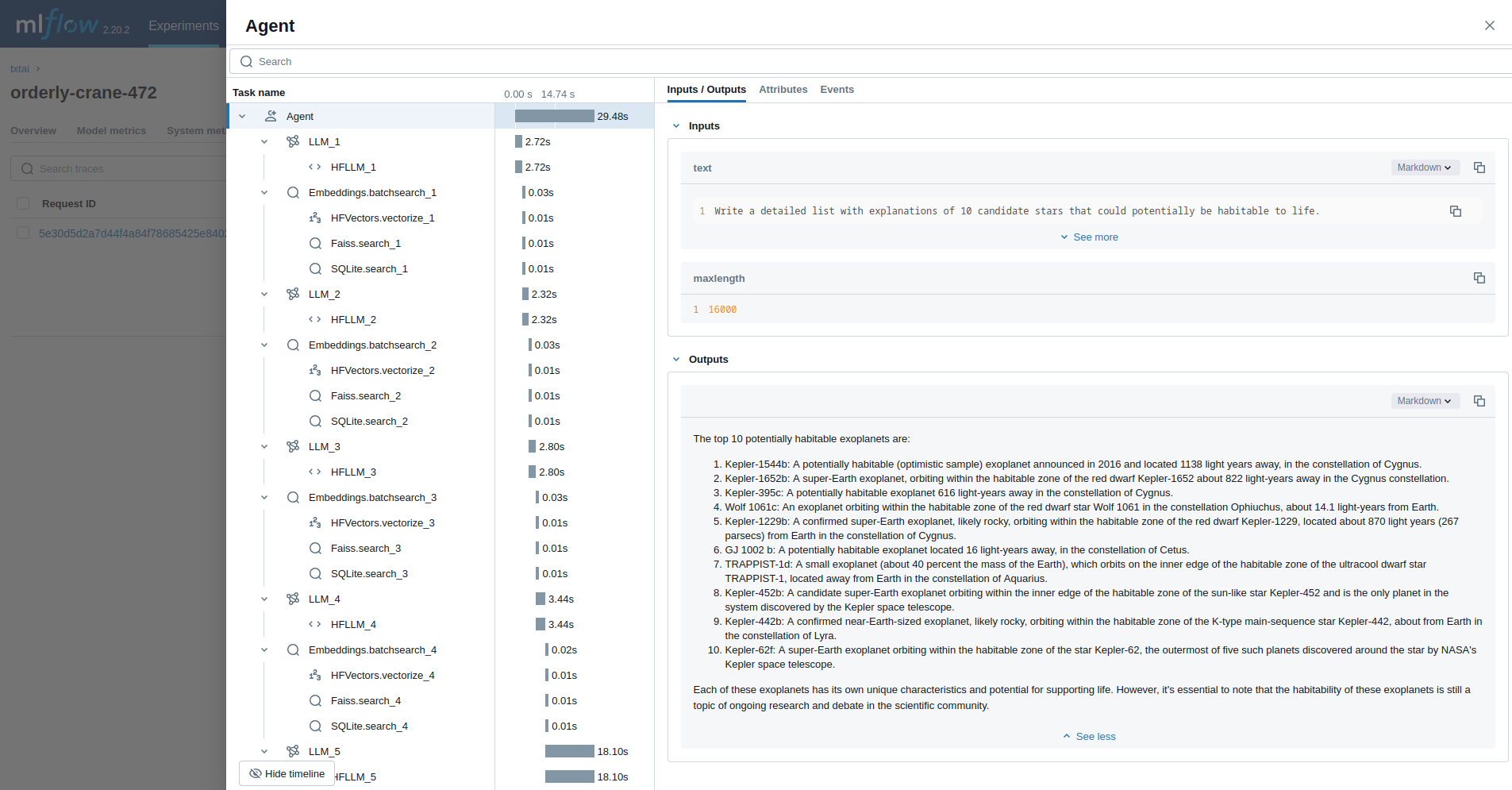
The last example runs a txtai agent designed to research questions on astronomy.
from txtai import Agent, Embeddings
def search(query):
"""
Searches a database of astronomy data.
Make sure to call this tool only with a string input, never use JSON.
Args:
query: concepts to search for using similarity search
Returns:
list of search results with for each match
"""
return embeddings.search(
"SELECT id, text, distance FROM txtai WHERE similar(:query)",
10, parameters={"query": query}
)
embeddings = Embeddings()
embeddings.load(provider="huggingface-hub", container="neuml/txtai-astronomy")
agent = Agent(
tools=[search],
llm="Qwen/Qwen3-4B-Instruct-2507",
max_steps=10,
)
researcher = """
{command}
Do the following.
- Search for results related to the topic.
- Analyze the results
- Continue querying until conclusive answers are found
- Write a Markdown report
"""
with mlflow.start_run():
agent(researcher.format(command="""
Write a detailed list with explanations of 10 candidate stars that could potentially be habitable to life.
"""), maxlength=16000)

Read more
Check out the mlflow-txtai project to see more examples.